INNOVATIVE ACTIVITIES
The Company has an innovation development programme of PJSC Rosseti South for the period of
The goal of the Programme is to transition Rosseti South to distribution grids of a new technological mode with qualitatively new characteristics of reliability, efficiency, accessibility, manageability, and customer focus of the distribution grid complex.

Transition to digital substations with the highest voltage class of 35–110 kV
Transition to digital smart grids with a distributed intellectual automation and control system
Transition to integrated business processes and automation of control systems
Utilisation of new technology solutions and materials in power engineering
MAIN COMPLEX INNOVATION PROJECTS IMPLEMENTED IN 2023
Transition to digital smart grids with a distributed intellectual automation and control system
Complex innovation project for installation of smart electricity metering devices
The technology provides for effective integration of commercial (electricity volumes) and technological (current, voltage and frequency) measurement functions in a single digital device with transmission of information data to upper control levels, as well as control of switching devices by external command or according to a predetermined algorithm.
The installation of SEMDs at metering points ensures:
- Electricity metering by voltage level of
0.2–0.4 kV - Automated calculation of power imbalances and identification of power loss centres
- Integration of information data from the APCS and Operational information complexes of dispatchers
- Remote load disconnection of 0.4 kV power consumers
- Improved efficiency of electricity services through higher share of useful electricity supply generated by electricity metering devices included in the smart data collection and transmission system
The actual utilisation of material resources in 2023 is equal to the planned value and amounted to RUB 238.9 million.
Development of the innovation development management system and establishment of innovation infrastructure
Application of the knowledge management system (hereinafter referred to as KMS) in the process model for managing technological and innovative development of PJSC Rosseti South.
The technology involves improving innovation development management systems by changing and upgrading the efficiency of Rosseti South’s business processes and creating an electronic information knowledge base with its integration with the corporate electronic knowledge base of the Rosseti Group (FSBI Russian Energy Agency of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation).
The introduction of the KMS at Rosseti South made it possible:
- To increase labour productivity by reducing time spent on searching for and replicating information data, improving the quality of technical decisions made, and enhancing the efficiency of knowledge exchange between various structural divisions of PJSC Rosseti South and third-party organisations
- To promote the practices of mentoring, self-training and internal training of Rosseti South employees, as well as to raise the efficiency of material expenditures on R&D
- To boost the rationalisation and inventive activity of PJSC Rosseti South, as well as the efficiency of material investments in the training and professional development of its employees
- To ensure the preservation and exchange of experience in the operation of various electrical equipment, as well as the implementation of pilot projects with an assessment of their effectiveness and prospects for roll-out
- To ensure that errors in the operation and maintenance of electrical equipment can be reduced
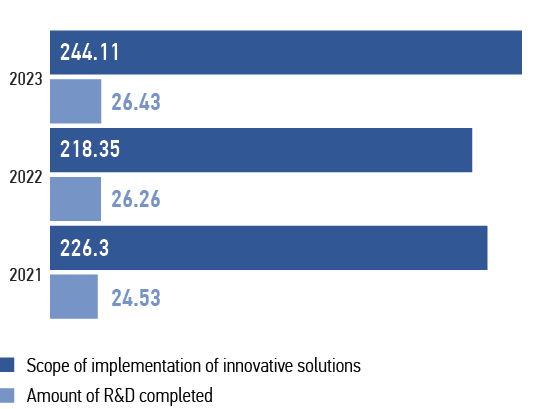
Areas of innovative development | Cost plan, RUB mln (excluding VAT) | Actual cost, RUB mln (excluding VAT) |
|---|---|---|
Transition to smart substations of | 16.400 | 0.000 |
Transition to digital smart grids with a distributed intellectual automation and control system | 134.350 | 238.900 |
Transition to integrated business processes and automation of control systems | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Utilisation of new technology solutions and materials in power engineering | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Promotion of the system of development and introduction of innovative products and technologies, R&D activities | 38.710 | 26.432 |
Development of the innovation development management system and establishment of innovation infrastructure | 5.210 | 5.210 |
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
The implementation of the R&D Programme is one of the key innovative development areas for the power grid complex. This Programme covers measures to ensure reliable (uninterruptible) and high-quality power supply of electricity consumers, reduction of material expenses for repair and maintenance of overhead transmission lines with a minimum expenditure of money for repair and maintenance of the system equipment, and transition to digital signal transmission at all levels of control over substations.
The following R&D activities were performed in 2023.
1Development of an automated digital radiographic complex for monitoring the condition of high-voltage equipment in operation. The work is aligned with the terms and conditions of the agreement concluded between PJSC Rosseti South and JSC Inspection for Control of Technical Condition of Electric Power Facilities (JSC Technical Inspection of UES).
The planned effect from R&D: creation of a mobile instrument-analytical complex on a self-propelled automobile chassis will provide:
- Operational radiographic control of the technical condition of high-voltage electrical equipment at the place of its installation without dismantling and opening
- Increased informativeness of diagnostics and automated transmission of survey results in electronic (digital) format to the level of information data collection and/or local management of PJSC Rosseti South
2Development of a methodology for assessing the compliance of current transformer error with datasheet data on the basis of unbalanced readings of electricity meters for the transition from periodic calibration of current transformers to condition-based calibration. The work is aligned with the terms and conditions of the agreement concluded between PJSC Rosseti South and JSC Scientific and Technical Centre of the Federal Grid Company of the Unified Energy System (JSC STC FGC UES).
Planned effect from R&D: the following technical and economic effect is expected upon implementation of the developed methodology based on the results of R&D:
- Transition from periodic calibration of current transformers to their condition-based calibration, which will result in reduction of organisational and technical measures for calibration at the place of their installation
- Reduction in the number of operations by switching devices to bring the connections into repair directly for calibration of current transformers in technical metering schemes, which, as a consequence, eliminates the risk of deteriorating the reliability of installed electrical equipment
- Reduction in the amount of electricity supply shortfalls and revenue shortfalls of Rosseti South for the provision of electricity transport services, as well as the amount of material costs for calibration and use of motor vehicles
- Improvement of reliability of the installed electrical equipment, as well as reduction of labour costs of the involved operational and maintenance personnel for the organisation of works on calibration of current transformers, especially in the period of large-scale production of works

